Resumo
- A inteligência artificial (IA) está sendo cada vez mais adotada em vários setores, incluindo UX / UI, que tem o potencial de gerar uma ampla gama de opções de design de forma rápida e eficiente, ajudando a estimular a criatividade e informar as escolhas de design.
- Plataformas como a Midjourney oferecem ferramentas baseadas em IA para geração de imagens, incluindo designs de interface do usuário.
- Experiência prática com o Midjourney mostrou que ele pode gerar designs de interface do usuário visualmente atraentes, mas há limitações em termos de atenção aos detalhes, acessibilidade e funcionalidade, e uma completa falta de UX.
- Os projetos gerados por IA podem ser usados como ponto de partida para projetos rápidos ou usados como referências para projetos mais complexos, mas um toque humano ainda é necessário para uma melhor experiência do usuário.
- Saber como equilibrar o uso da IA com um processo adequado de UX / UI pode resultar em grandes projetos.
A inteligência artificial (IA) vem deixando sua marca em diversos setores, com aplicações que vão desde a geração de conteúdo até a criação de voz e vídeo. À medida que mais e mais indústrias adotam essa tecnologia de ponta, a maneira como pensamos sobre as possibilidades está evoluindo. No entanto, muitas questões surgem a partir dele, de preocupações éticas a medos de perda de emprego.
Nas últimas semanas e meses, a IA também entrou no mundo do UX/UI design, com muitos designers se perguntando se poderia ser uma ferramenta viável para gerar ideias de design e simplificar fluxos de trabalho, e outros criticando o uso da IA e suas preocupações que isso poderia causar para a nossa área.
Pelo lado positivo, um dos principais benefícios do uso da IA no design da interface do usuário é desbloquear uma infinidade de novas oportunidades como nunca antes, com sua capacidade de gerar uma ampla gama de opções de design de forma rápida e eficiente. Isso pode ser especialmente útil ao iniciar um novo projeto e tentar ter uma noção da direção que ele poderia tomar.
By feeding design concepts and styles into an AI system, designers can get a diverse set of ideas and inspiration that can spark creativity and help inform their own design choices. Website, landing pages, dashboards, mobile apps – there are lots of possibilities to be discovered and generated, and we are already seeing many people using those tools for UI.
Esta tecnologia está permitindo que designers explorem novos horizontes, gerem um número quase infinito de possibilidades e lhes deem a liberdade de criar como nunca antes. Com a IA, parece que o céu é o limite. Ou talvez não?
Nossa experiência prática gerando interfaces de usuário com IA
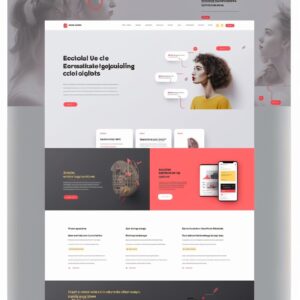
Uma plataforma que oferece ferramentas baseadas em IA é o Midjourney, um canal do Discord aberto ao público onde você só precisa digitar uma descrição ou comando e a IA gera diferentes versões para você.
It’s not exclusive to UI, it can be used for any kind of image generation, such as ultrarealist photos, illustrations, fantasy images, and even images like logos. Actually, UI generation is still a small portion of what is generated, mostly because it was only possible after their new version 4 elevated the powerful tool to a whole new level.
We’ve had the opportunity to use Midjourney and were impressed by the convenience and flexibility it offers. After a few attempts trying to understand what would be a good prompt to reach great results, we were able to generate a few impressive visual-appealing UI designs generated by only typing some words.
Testando com sites simples
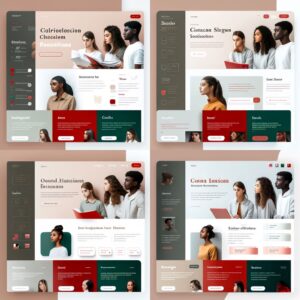
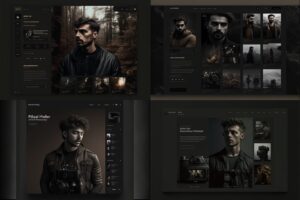
Primeiro tentamos um portfólio simples online para fotógrafos e escolhemos um dos gerados para avançar:
As it can be seen, the AI tool can generate a visually appealing interface, however, it doesn’t focus on details. Buttons, small elements, and especially text are misformed making the interface unusable the way it is. Don’t expect it to deliver a ready-to-use interface, it can’t and it won’t be a good interface.
No entanto, os resultados são interessantes e úteis para iniciar o projeto, considerando que ele precisará de algum trabalho para ser uma interface funcional.
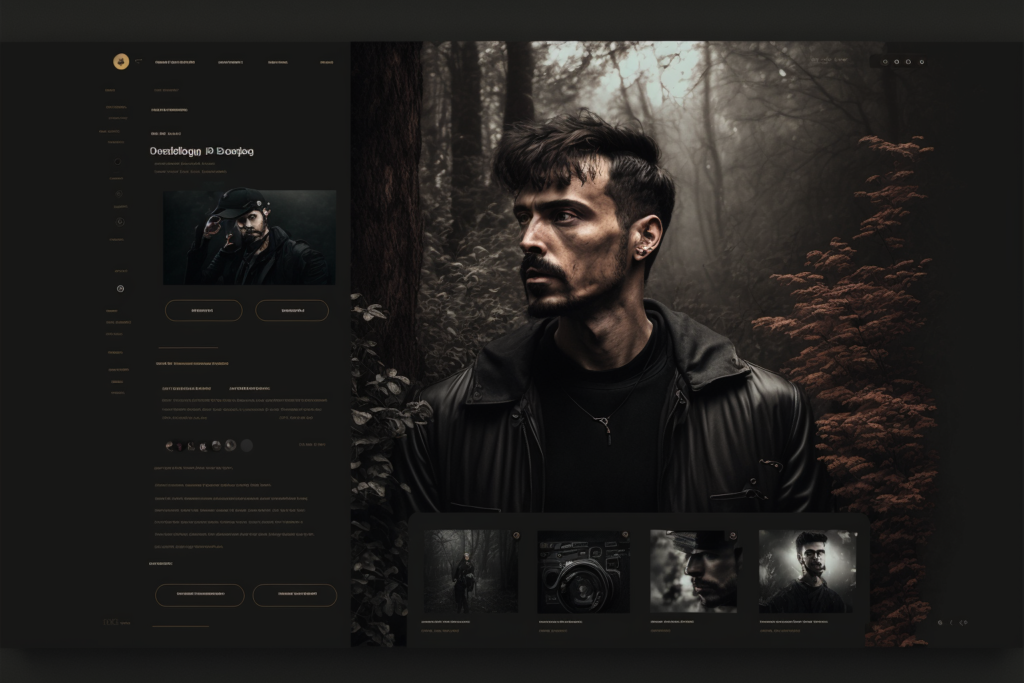
We then replicate it on Figma to grasp an idea of what would be the process of using AI-generated websites for a real project – this is the first stage where a human needs to step into the process.
Nosso foco era criar uma interface semelhante, mas notamos que alguns elementos ainda não eram tão intuitivos, e é aqui, novamente, onde um ser humano deve intervir e entender o que é necessário para uma melhor experiência do usuário.
We come up with a second version, just playing around with some elements, making the category selector more intuitive – it wasn’t clear if it was a category selector, and what were the other categories.
Embora tivemos que fazer algumas mudanças, achamos que o Midjourney fez um ótimo trabalho com uma interface simples, como um portfólio. Em casos como este, ele poderia ser usado como um começo para projetos rápidos.
However, how good would it be in different projects? We decided to go to something a bit more complex, as we were certain that it wouldn’t provide an almost ready-to-use design.
Um site um pouco mais complexo
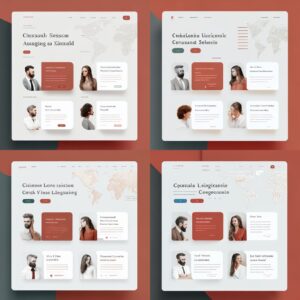
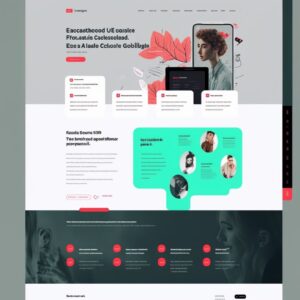
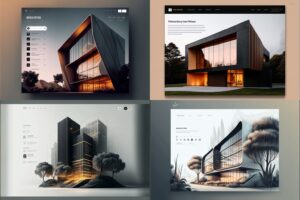
Pedimos um site de escola de idiomas solicitando uma paleta de cores específica e geramos várias alternativas que foram muito interessantes. Os resultados foram muito agradáveis e incluíram as cores que pedimos.
However, none of the generated websites could be used as an initial base since the content wouldn’t be the one that the AI tool generated. The content for this specific project would be very different from the generated image, and as we know in UX/UI, content is king and the interface needs to fit the content, not the other way around. This is the case where the AI-generated UI images would be used as (great) inspirations when creating a mood board, but not as a base for the first draft.
Gerando um redesign de um site com muito conteúdo
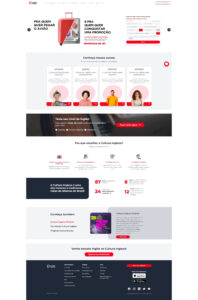
Para testar outra possibilidade, usamos um site existente, www.culturainglesa.com.br, para ver a extensão das capacidades do Midjourney de duas maneiras: se a plataforma pode usar uma imagem como referência e produzir um bom resultado a partir dela; se ele pode replicar a página como mencionado, fazendo com que a interface se encaixasse no conteúdo.
The results of several attempts with different prompts can be seen below – impressive nonetheless, it got the essence a bit and used the black and red of the brand, however, it’s clear that it’s still lacking a more human vision, content fit, and compliance with the branding as well – it used a yellow and green that was not part of the original website but were included in photos.
Reunimos pontos de destaque das opções mais interessantes e projetamos uma versão rápida usando o conteúdo original e as cores corretas da marca:
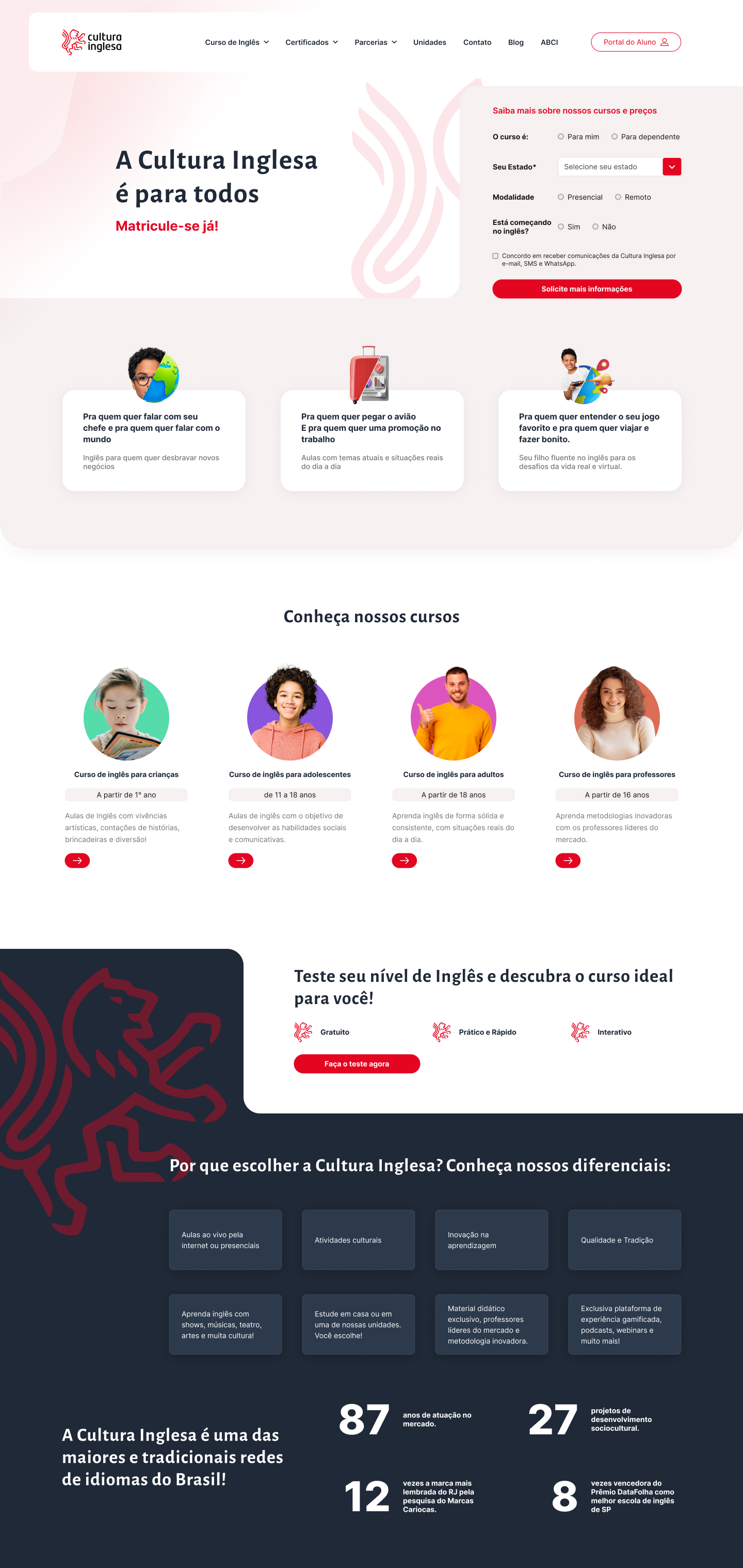
Overall we thought that it helped us to create a visually appealing interface, serving as original inspiration during our mood board process, saving us time. However, it took longer than just replicating the interface as we did with the photographer’s portfolio.
In cases like this, it’s valid to use AI-generated images as references for the designer’s work rather than a quick tool to generate final interfaces.
Pushing AI to its limits – a more complex UI for a dashboard
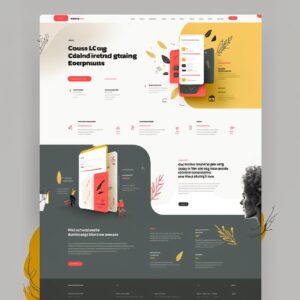
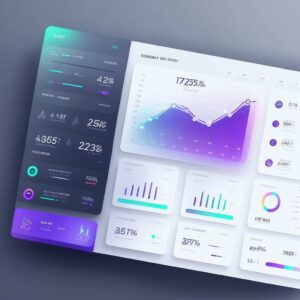
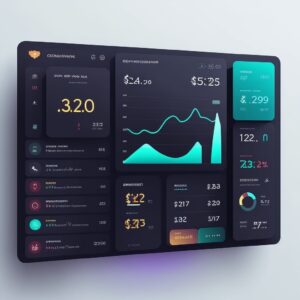
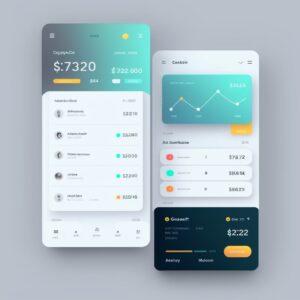
Em um último teste, decidimos ver como ele lidaria com uma interface mais complexa para um produto digital, então pedimos para criar uma dashboard de uma fintech, incluindo informações como cartões de crédito, transações e botões de ação rápida. Obtivemos resultados visualmente impressionantes na primeira tentativa:
Os resultados foram muito próximos do que se esperava: uma bela dashboard que pode facilmente ir para um mood board de aplicativo de fintech.
No entanto, aqui é onde a UX está muito prejudicada
- Falta de acessibilidade em vários elementos: elementos que têm uma relação de contraste muito baixa que os torna difíceis de ver e ler os textos
- Perda de foco: em algumas partes tem muita informação acontecendo
- There’s no user flow to make a proper evaluation of how, where, and if elements can be presented.
We see again how important a proper UX process is needed to bring those AI-generated to life. A designer can understand the users’ pain point and their needs in order to plan the project with personas, user flows, customer journey maps, and other tools that will guide the work toward a more intuitive user interface.
Mais interfaces geradas por IA
Benefícios e limitações da IA para UX/UI Design
Como acontece com qualquer ferramenta de IA, ela não pode entender completamente ou replicar as nuances e complexidades do design centrado no ser humano. Os projetos gerados por essas ferramentas não estão necessariamente prontos para uso como estão e devem ser vistos como um ponto de partida e uma fonte de inspiração, em vez de um substituto para o trabalho e o julgamento humanos.
É importante lembrar que o UX/UI design tem tudo a ver com a criação de uma experiência perfeita e intuitiva para o usuário. Isso significa que o design deve ser adaptado às necessidades, motivações e comportamentos do público-alvo que interagirá com ele, o que um sistema de IA não pode compreender ou antecipar.
Cabe ao designer trazer um toque humano, empatia e compreensão para o processo de design, usando sua própria experiência e julgamento para tomar decisões de design informadas. Somente por meio de pesquisa, testes e feedback do usuário você pode coletar insights sobre o que funcionará melhor para eles.
A capacidade de qualquer ferramenta de IA de gerar resultados precisos também depende da sua capacidade de descrever o que você quer com as palavras certas. Tivemos que tentar vários comandos diferentes para começar a ter uma ideia de como escrever bons comandos. E mesmo assim, a cada nova ideia que surgiu, tivemos que fazer mais tentativas até ficarmos satisfeitos com os resultados.
Outra limitação é a impossibilidade de extrair elementos e imagens das imagens geradas por IA, pois não são separados, você recebe um arquivo de imagem PNG. Na maioria das vezes, mesmo com projetos simples como o portfólio do fotógrafo, designers precisam usar outros elementos ou até mesmo tentar gerá-los separadamente, por exemplo, uma imagem de fundo de banner.
Designers precisam aprender como e quando usar a IA
As ferramentas de IA devem ser vistas como um complemento ao processo de design, ajudando designers a explorar uma gama mais ampla de opções e possibilidades antes de aprimorar a direção do design. Não vai tirar nossos empregos (pelo menos por enquanto), mas abraçar essa nova tecnologia requer um senso crítico.
Para criar designs verdadeiramente eficazes e centrados no usuário, designers devem sempre estar sintonizados com as necessidades e comportamentos de seu público-alvo, usando uma combinação de pesquisa, testes e sua própria experiência para orientar as decisões de design.
Desde que estabeleçam um equilíbrio entre a conveniência e a eficiência de ferramentas de IA como o Midjourney e as perspectivas e insights exclusivos dos usuários humanos, designers podem criar designs verdadeiramente eficazes e centrados no usuário.
No geral, nossa experiência com o Midjourney foi positiva e achamos que pode ser uma ferramenta poderosa e um recurso valioso para ajudar designers com tarefas específicas, desde com cautela e não dependendo muito delas.
It’s also clear that it’s not even close to the end of our jobs, given there are several limitations that may not be resolved soon – or possibly ever? Who knows.
obs.: o banner também foi criado pelo Midjourney 🙂
Já se perguntou como melhorar a experiência do usuário do seu produto digital? Como deixá-lo mais intuitivo e fácil de usar, convertendo mais e retendo mais usuários?
O design da experiência do usuário é uma disciplina cujo foco é a criação de uma experiência acessível e agradável para os usuários de produtos e serviços digitais. É um campo vasto com muitas nuances, mas muitas vezes é simplificado demais pelo público em geral na forma de conselhos como “Basta colocar um rostinho bonito no seu site!”
The best user experience doesn’t come from an algorithm that analyzes data and figures out the best way to serve your users. Instead, it results from an intimate knowledge of users and the way they interact with technology, you need to understand them. By understanding their needs, habits, and goals, you can design a better user experience.
Dito isto, a experiência do usuário não é puramente sobre tecnologia, você precisa considerar a jornada do usuário. Isso significa saber qual é o ponto de partida do usuário e quais são seus objetivos.
Com a experiência do usuário, você também deve pensar em como os usuários se sentem ao usar seu aplicativo. Eles se sentem confortáveis e bem-vindos? Ou eles se sentem distraídos, frustrados ou irritados?
Aqui estão algumas dicas sobre como criar uma melhor a experiência do usuário.
Comece por entender as necessidades e demandas de seus usuários com uma pesquisa de UX

A melhor maneira de começar a melhorar o UX do seu produto é focar no usuário que o utiliza antes que qualquer design e implementação sejam feitos, seja para iniciar um novo produto digital ou para melhorar um já existente.
Se você não sabe o que seus usuários querem e precisam, o produto final provavelmente será inferior. Estude seu público-alvo para obter informações sobre o que eles desejam para poder desenvolver uma interface especificamente para esse público.
Isso pode ser alcançado realizando uma pesquisa de UX para coletar dados e particularidades sobre o que as pessoas querem e precisam do seu produto, como elas interagem com a interface e seu comportamento ao longo da jornada do usuário dentro do produto digital.
Uma pesquisa de UX pode envolver um questionário, grupos de foco, testes de usuários ou entrevistas para coletar informações sobre seus dados demográficos, comportamento e problemas que enfrentam. Os dados são priorizados de acordo com o que é mais incômodo para os usuários e usados para informar e auxiliar na tomada de decisão para os produtos e propor soluções adequadas.
Conduza uma Auditoria de UX

Enquanto isso, uma auditoria de UX é um processo de inspeção e avaliação do design de um produto existente. Basicamente, um mergulho mais profundo em seu produto digital. É uma análise sistemática da experiência do usuário com o objetivo de identificar áreas de melhoria e alinhar os designers com a estratégia certa.
Ela ajuda a entender como as pessoas usam seu produto e como elas se sentem sobre ele, descobrindo possíveis problemas e sugerindo possíveis soluções. Uma auditoria de UX é uma ótima maneira de dar uma segunda olhada no seu produto e ver o que pode ser melhorado em termos de UX.
Uma boa Auditoria de UX ajudará você a criar um produto que as pessoas adoram usar.
Mantenha a simplicidade, foque na funcionalidade

Ao projetar uma interface para um produto, é importante mantê-la simples. A ideia de simplicidade no design para um UX melhor não é apenas fazer menos, mas fazer o que é importante, ser objetivo e fornecer informações e orientações diretas em uma interface limpa que orientará os usuários a atingir seus objetivos.
The simpler an interface is, the easier it will be for users to navigate and the less likely they will bounce. Because of that, it’s important to focus on the content and functionality rather than focusing on purely visual elements. They are important as well, a visually appealing interface helps build trust and express professionalism, but they are rather an add-on.
It’s important to understand that simplicity is not the same as minimalism design. It can definitely be used if it suits the overall look ‘n feel, but we can also achieve simplicity by creating an atmosphere that is free of clutter, taking away what does not add value to the interface. Increasing whitespace is also helpful to legibility and it’s faster and easier to find what users need.
Acessibilidade

Acessibilidade significa garantir que qualquer pessoa possa usar seu produto, independentemente de suas habilidades físicas ou cognitivas.
Com o aumento de pessoas com deficiência e o uso geral da internet, onde 67% da população mundial tem acesso à internet, a acessibilidade tornou-se uma expectativa padrão em produtos digitais.
Algumas mudanças simples podem fazer uma grande diferença para muitas pessoas. Ao fazer pequenos ajustes você pode criar uma experiência verdadeiramente acessível para todos. Legendas de imagens e textos alternativos, por exemplo, podem fazer com que os deficientes visuais entendam o que é mostrado na imagem pois o leitor de tela irá ler os textos inseridos como descrição do que a imagem representa.
Documentos existentes como o WCAG 2.0 (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) do W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) ou a Seção 508 do ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) fornecem recomendações sobre como criar sites e aplicativos acessíveis.
A falta de acessibilidade é até caso para ações judiciais. Nos EUA, as Diretrizes ADA mencionadas anteriormente são um requisito para a maioria das empresas. Não estar em conformidade com a ADA pode levar a ações judiciais. Milhares de processos estão sendo apresentados todos os anos e isso pode significar de 10 mil a milhões em perdas.
Mantenha a consistência do design ao longo da jornada
Quando projetar seu produto, it’s important to continue certain patterns through the user flow. Elements, colors, fonts, copy, icons, interactions, and overall look ‘n feel should be homogeneous and repeat themselves throughout the product. This creates a cohesive experience for your users and allows them to navigate through your product with ease.
A consistência do design proporciona uma sensação de familiaridade e conforto ao usuário e reduz as chances de se perderem. Evita ter que reaprender um padrão para conteúdo semelhante e ficar confuso, melhorando a usabilidade geral.
We do that by defining a scalable design system right at the beginning of the project, keeping the consistency of the elements even if they are modified later. It’s easier to scale the product in the future as well.
Applying the best practices for UI also helps users recognize widely used patterns that were already extensively validated. It’s a way to start off on the right foot especially if you for any reason can’t do a UX research before designing the interface.
Peça feedback ao usuário

Without knowing what users are experiencing while using your product, there’s no way to improve it. If they have a bad experience and don’t have a way to tell you about it, you might lose the user and don’t even know why.
There are several ways to ask for feedback from users and it all depends on how they use your product, but the most important is to ask it promptly. Have a feedback tool right inside the product, or ask when the user is leaving or after a specific event, such as at the end of a journey as a purchase in an e-commerce. Just the fact that you’re asking for feedback shows that you care about the user experience.
O custo para adquirir um cliente é muito maior do que manter um. Porém, pedir feedback é gratuito e uma das maneiras mais fáceis de melhorar a experiência para manter os usuários satisfeitos.
Conclusão
UX design é um campo em crescimento que está em constante evolução. Há muitas maneiras de melhorar a UX para o seu produto digital, e provavelmente a maioia delas é preciso um time de especialistas para implementá-las.
A Pengreen Design é especialista em melhorar a usabilidade de produtos digitais e pode realizar uma Auditoria de UX para seu produto digital. Ajudamos as empresas de desenvolvimento de software reduce their frustrations with bad conversions rate and low satisfaction from customers by understanding users’ behavior and delivering the right content they need and expect. Our team of experts can go through your digital product and identify potential issues that may be driving customers away.
Because of the pandemic, Germany was offering double incentives for electric car purchases, and seeing it as a good opportunity, a German wanted to exchange his Ford Kuga for a Tesla Model 3 with autopilot, the entry model of Elon Musk’s automaker.
He then proceeded with the purchase, added his details and credit card, and clicked “confirm” to place the order with Tesla. But nothing happened, the button continued as it was, no message was shown, nothing different that could indicate that the order was being processed or even that it had already been placed or denied. As a result, he clicked again, as it might simply not have gone. And again, and so on 27 other times within two hours – what a persistent person!
After several attempts, the site finally changed and processed the request – not just one, but all 28 attempts, totaling 1.4 million euros for the 28 Tesla Model 3. Not only that, but if the German would ask to cancel the 27 extra orders, he would still have to pay 100 euros for each cancellation, totaling 2700 euros more than just the 100 euros deposit expected by ordering just one car.
Este é um claro erro em fornecer uma boa experiência do usuário e infringiu duas Nielsen’s 10 heuristics.
- A primeira é evitar que o usuário cometa erros. Ao clicar em um botão que envia informações para processamento, imediatamente deve-se desabilitá-lo para não ser clicado novamente.
- A segunda é sempre e rapidamente informar o status do sistema através de feedbacks claros. Após o botão ser clicado é necessário informar ao usuário que o site está processando as informações e pedir para que não feche a tela para evitar erros.
Há erros também no processamento que não afetam diretamente na UX porém, como visto, afeta indiretamente. A lentidão em processar o pedido e a falha ao permitir que fossem processados os outros 27 pedidos sem que nenhum retorno tivesse sido dado para o primeiro também foram determinantes para o erro humano.
Isso mostra que equipes de design e desenvolvimento devem trabalhar juntos para evitar situação como essa.
No final, o alemão ligou desesperado para a empresa e, entendendo o erro acontecido, a Tesla reembolsou os 2800 euros pelo depósito obrigatório e convidou o homem a fazer seu pedido novamente.
A questão é: ele vai comprar novamente depois dessa falha? A confiança é destruída e o cliente foi perdido?
Precisamos evitar que esse tipo de erro ocorra em primeiro lugar, em vez de corrigí-lo mais tarde. O custo será mais alto, com certeza, não apenas em desenvolvimento interno para arrumá-lo, mas a perda em faturamento e de consumidores, além de ter que reparar a reputação que foi afetada. Uma boa estratégia de UX e um design de produto bem conduzido podem evitar muitos problemas triviais como esse.
Veja mais exemplos de UI problemáticas
Quer saber se o seu site apresenta falhas de UX?
UX issues are more common than we can think and some of them we don’t see unless they happen. Pengreen Design has an experienced team of designers ready to help you. We are listed at Best Tech Websites Of 2020 (So Far).
Desbloqueie todo o potencial do seu produto digital com nossa Auditoria de UX! Uncover hidden design flaws that might be hindering your product’s success, some of which you may not even be aware of.
First off, user experience design is not the same as or similar to marketing and vice versa. Actually, many times UX professionals even work against marketers and the last ones also go against the first ones sometimes. Personally, I already had a tough relationship with a marketer who wanted to sell at any cost and disregarded my UI/UX considerations, but this is part of the job and we need to understand both sides to accomplish a successful project.
Yes, they have points in common. To an extent, both have an ultimate goal of increasing conversions or keeping current users faithful to the service/product, both help the business and both need a deep analysis of human behavior to draw a good strategy. They do not exist without people’s input. But they have many (and important) distinctions regarding the ways to achieve these mutual goals.
Users VS Metrics, Satisfaction VS Revenue – It’s a tough balance. And they MUST work together in order not to jeopardize the other.
Let’s first understand the concepts:
User Experience (UX)
Consists of researching the users’ behavior and improving the experience they have by creating the best, most intuitive, easiest-to-use interface, where the flow is consistent and clear (and just an addendum, it does not apply only to web and mobile interfaces, this can be applied to the installation of a product, for example). The primary goal is to design with the user in mind, which eventually leads to the secondary goal (and kind of primary to who is paying the bill): to improve the conversions or keep users faithful to the service/product by providing a pleasant experience.
“User Experience encompasses all aspects of end-user interaction with the company, its services, and its products.”
Don Norman and Jakob Nielsen
Marketing
It’s the art of selling. The main goal is to increase conversions and consequentially, increase the revenue. To do that, marketers have to persuade people to buy the product or service, they use seducing ads, many times hiding important information and exaggerating the qualities.
“Marketing is a question of persuading, seducing and attempting to manipulate people into buying products and services.”
Wally Olins
In summary, both must understand people’s psychology, but marketing treats people as potential customers and it is not much concerned about their experience – more about selling -, and UX treats people as users and cares about their satisfaction. And that difference is problematic.
When the problems start and how they should help each other
UX endlessly states that a good user experience should not confuse or trick the user, it should give all the information to the user and always provide clear instructions and paths so the user can choose what he wants to do with a full understanding of the content and consequences without surprises or frustrations.
UX should never take advantage of the lack of or misleading information. These strategies are often in marketing to try to trick users with the ultimate goal of SELLING – nothing wrong with selling, we need it, but there is a thin line between white-hat selling and black-hat selling.
A marketing campaign with a heavy selling goal can jeopardize the user experience by applying dark patterns. Dark patterns are strategies that aim to persuade people into doing something they don’t fully understand and may not even consciously want to do.
Examples of that can be: adding the user to a mailing list without consent (which is now illegal in many countries of the world, such as the whole of Europe, the USA, Brazil, etc.), seducing the user to buy a product without more information to a rightful and thoughtful decision, making customers to buy extended warranties or upselling products without proper or misleading information of them, etc.
Dark patterns can cause some controversial discussions. Sometimes it’s hard to say if something is or isn’t a dark pattern, and people can have different views – it’s a thin line separating dark patterns and good patterns.
Regardless of marketing strategies, developing a project that does not take into account the user can bring more harm to the company image than conversion. If the user has a bad experience before or after becoming a customer or falls short of what is promised when trying to use the product or service, or if they have somehow been deceived or have not given consent for some kind of extra service, they can get frustrated and the efforts to attract and keep a user will be wasted and will not have a sustainable return.
Even worse, this can create a bad reputation that will be difficult to reverse. The loss of irresponsible marketing without taking into account the user experience can be immense and leave damages of difficult and expensive repair.
At the same time, UX professionals need to understand the company and its goals. They need to understand what intrinsic value the company wants to pass to the user, who is the target audience, and develop an interface that matches that without damaging the user experience.
UX without business values is like a meticulously designed ship without a compass. It might be sleek, efficient, and well-crafted, but without a clear direction tied to the business’s values, it risks drifting aimlessly in the vast sea of possibilities. Just as a compass guides a ship to its destination, aligning UX strategy with business values ensures a purposeful and successful journey for the digital product in the dynamic market landscape.
For all that to happen, it’s essential to have clear communication between both teams to express the objectives that both teams have and the planning of those goals. Thus, the UX professional can offer the most viable options according to the information given by the marketers to obtain the desired result, always, of course, respecting the basic concepts of UX.
Basically, they must complete each other. UX should help marketers to make users convert more without making UX mistakes. Marketers should help UX professionals to understand how (and where) to lead the user to the desired goal by communicating the values of the company’s products and services.
Do you want a team that knows how to work with business goals?
We have worked for years with marketing agencies and teams and we know how to balance a good estratégia de UX to make any product succeed and avoid UX pitfalls. Pengreen Design is among the Top Web Design Agencies Of 2020 according to DesignRush.
1) “Recommended view” limiting how the user should view the interface.

Responsive Web design consists of designing and developing interfaces to respond to the user’s device based on screen size, platform, and orientation.
Not on this website. It asks the user to rotate the device to a landscape orientation instead of presenting the website nicely in portrait orientation.
Not enough to limit the orientation, when the website is finally shown after rotating the smartphone, the user is presented with a bad interface, clearly not optimized for mobile.

Solution
Don’t ever ask the user to adapt to your interface, your interface is the one that must adapt to the user’s device.
Optimize it to EVERY possible device, orientation, and platform.
2) Primary and secondary button styles got wrong
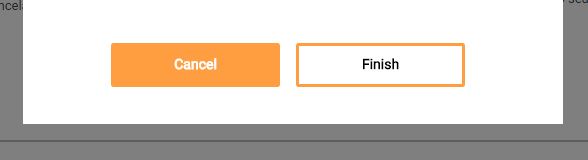
When two or more buttons are close to each other with different priorities, we need to differentiate them. As a best practice, we can use two options:
- The primary button has the interface’s primary color, which usually is a very striking or different color from the rest of the elements, and the secondary button has a less striking color, even gray in some cases.
The primary button has a background color whilst the secondary only has borders (which is debatable regarding ghost buttons, but this will be discussed in another post).
In this interface, they did the opposite for #2. The “finish” button, which should be the primary with the background only has borders. Whilst the “cancel” button which should be the secondary button has the background. The user can wrongly click on the “cancel” button without reading it properly thinking it’s the “finish” button.
Solution
Follow best practices to show very clearly to the user which button is primary and which is secondary.
3) Content that’s loaded after the interface is ready.
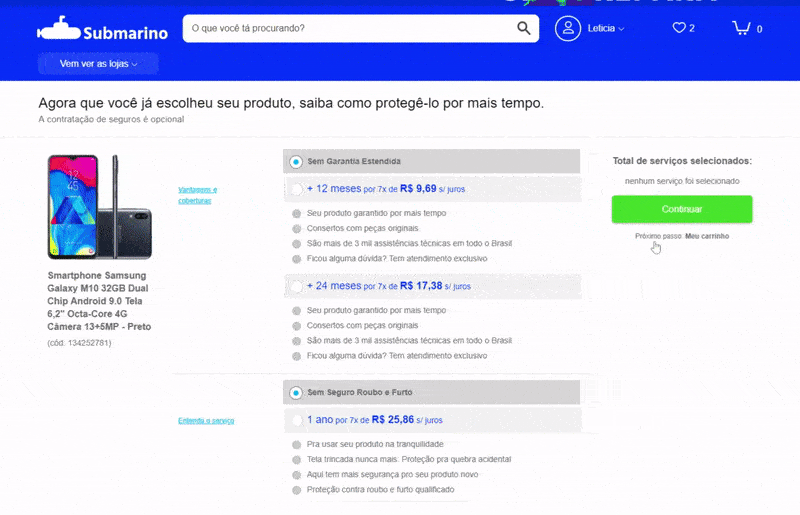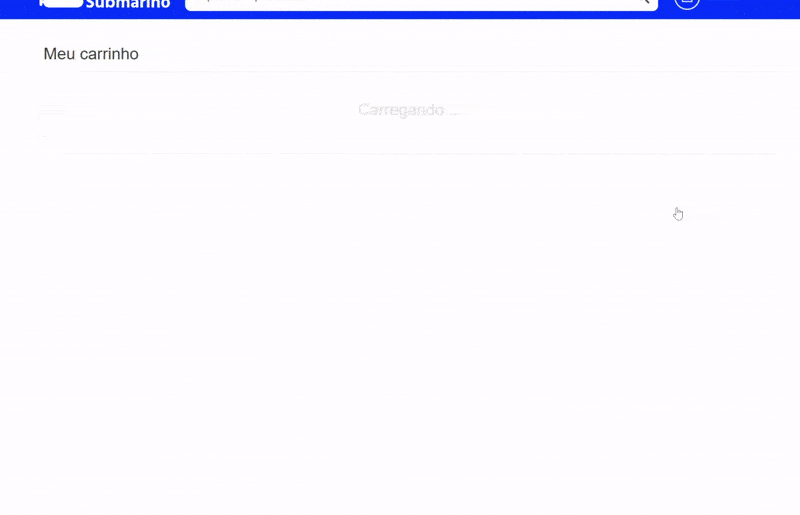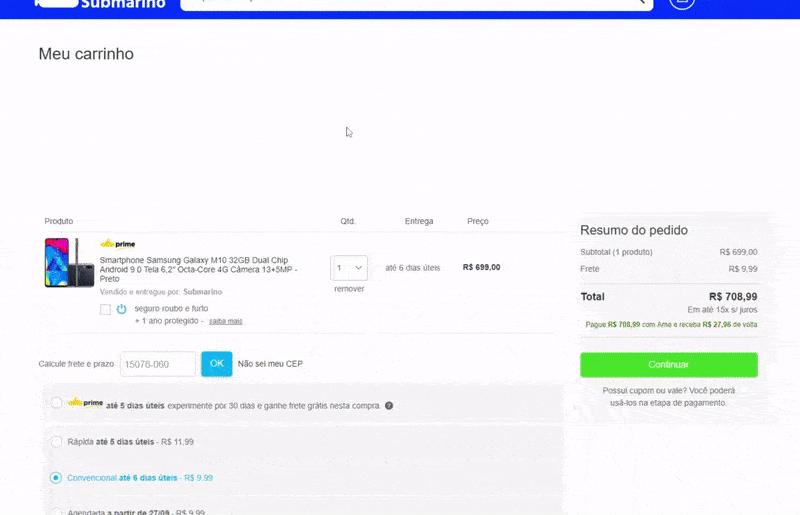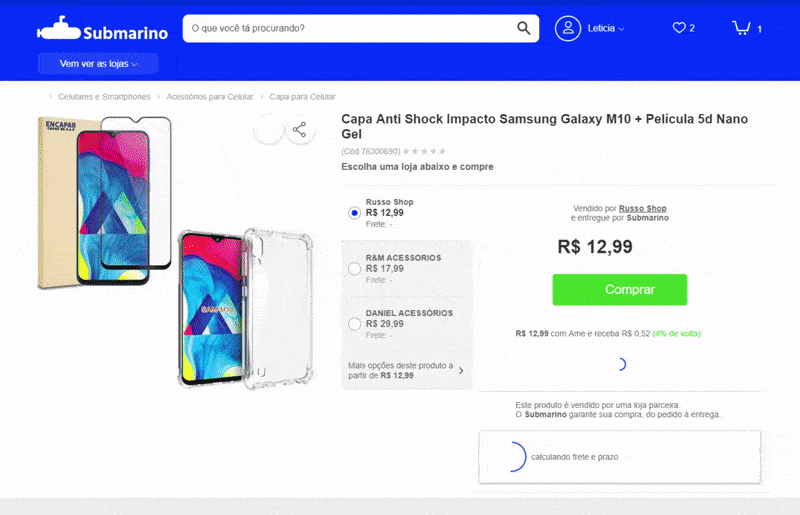
Sometimes we need to load content after the whole site is already there. But if that new content pushes everything down when being placed, you have a UX problem here.
Since the interface is already loaded, the user might be in the middle of an action, a click, a drag and drop. Having the content pushed down might cause unexpected behavior if the user clicks somewhere at the same moment that the new content appears.
The example below shows a shopping cart after adding a product. The e-commerce then loads related products on top of the cart after the content has already been loaded. If the user tries to change the quantity of the first product in the cart right at the moment that the related products are being loaded, it ends up clicking on one of them and going to the product page, frustrating the experience of buying that first product (Yeah, I did that many times, I always forget to wait for the related products, but this shouldn’t be an issue the user needs to deal with).
Solution
Either load everything together or leave a space beforehand where the new content will be loaded to avoid pushing the content down.
4) Ask the user not to do something.
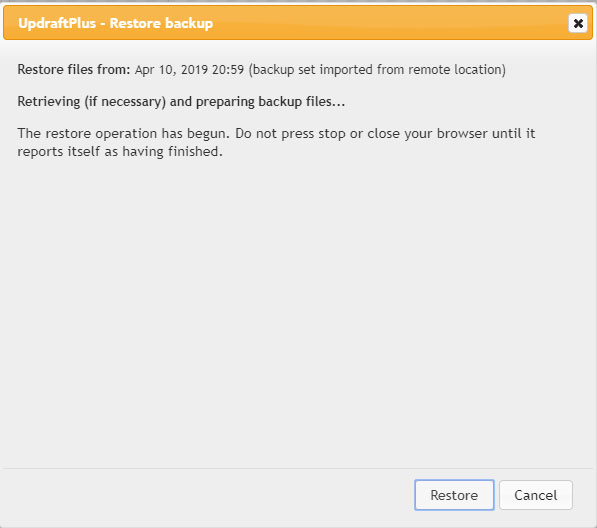
No, no, no. A big no-no. Never rely on the user’s good behavior to avoid errors. The interface itself MUST avoid users’ errors.
In this example, which is a WordPress plugin to backup and restore content, it asks the user not to click on the button until the restore is done, but leaves the button there! If the button is pressed, it can break the whole website. That’s a very bad UX, it relies on the user not to break their own website! Even a wrong click can cause a mess. And if the person who is doing it is a layperson, they will have to hire a developer to fix the website.
Solution
Keep the warning not to close the browser, but remove or disable (and style them as such) the buttons that can cause error after a dangerous action begins and add an alert if the user closes the window/browser informing that some action is taking place and it’s not recommended to close the browser.
P.S. Unfortunately, we can’t totally block the user from closing the window/browser in cases such as this, as part of a security policy implemented by browsers, but we can at least warn users of the risks.
Update: updraft released a new version of this interface and now it’s a lot more intuitive and it avoids such errors by removing the button off the screen.
5) Mislead user into paying more
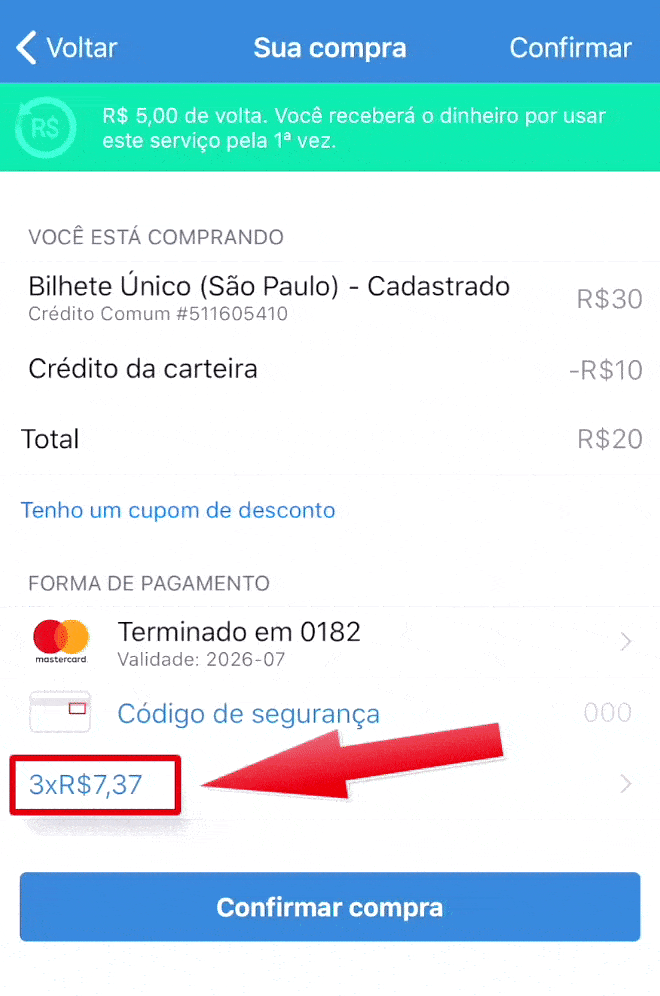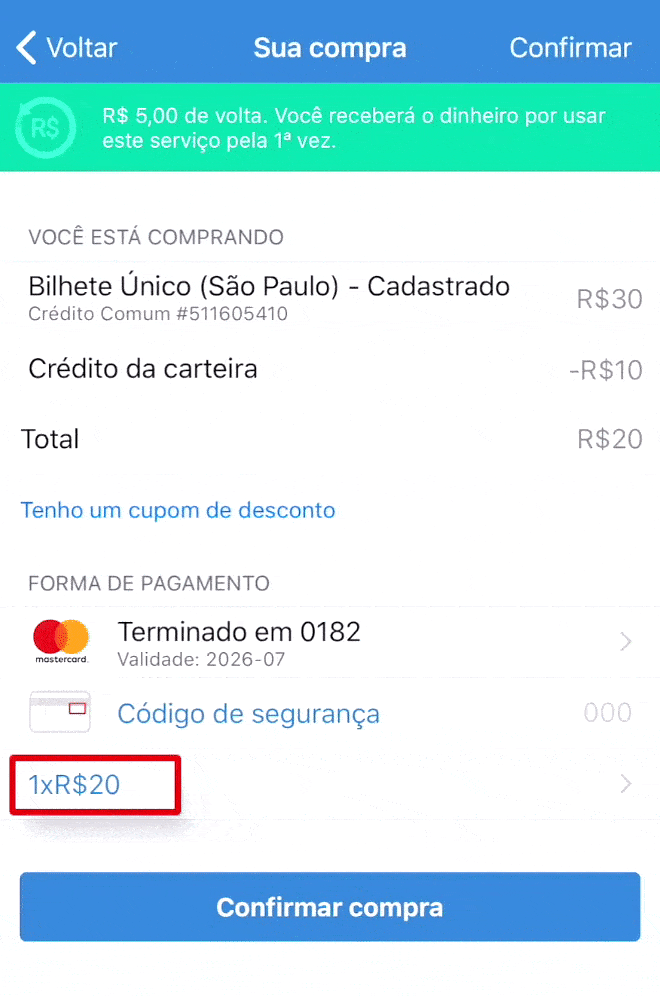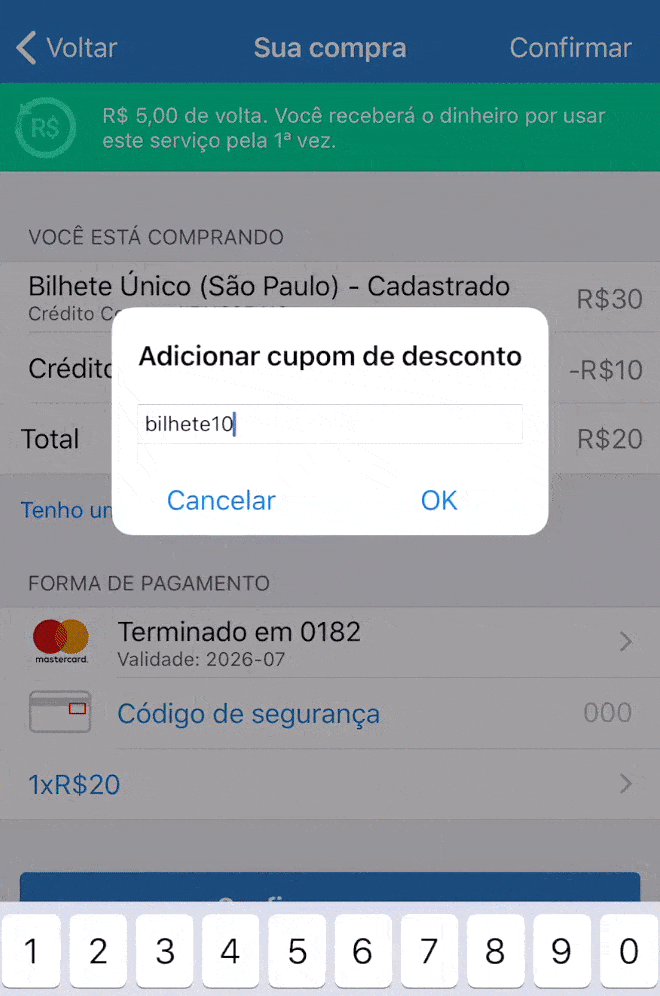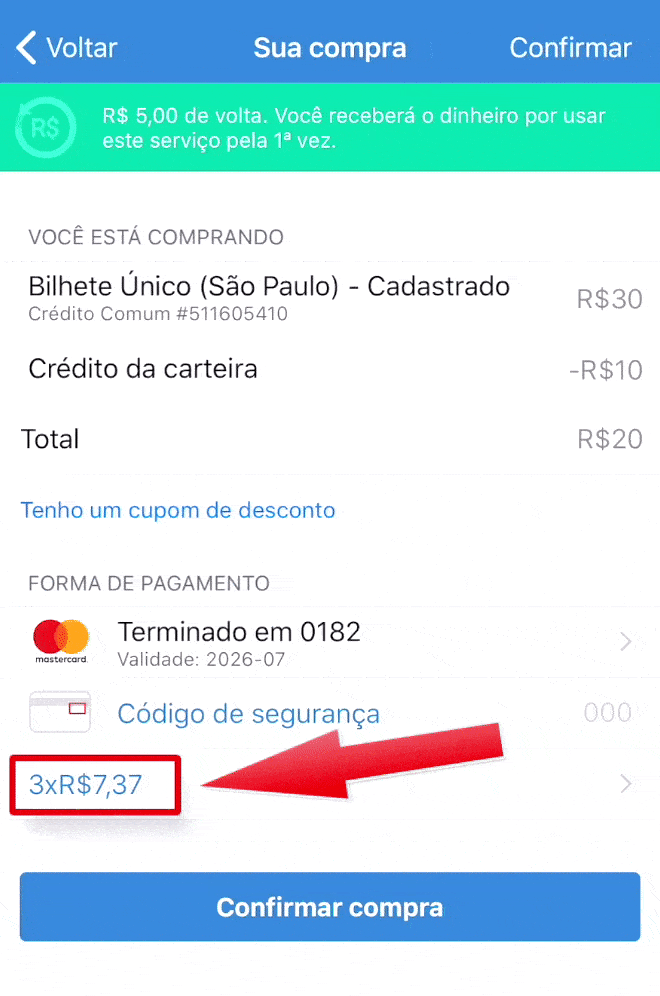
Here in Brazil purchasing in installments is very common, with or without interest clearly shown to the user.
On the app below, it shows first the value of R$ 20 in 3 installments (3 x R$ 7.37 = R$ 22.11, so you’re paying R$ 2.11 in interest). The user has then the option to change to 1x without interest. But if the user makes any other change like changing the credit card to pay or adding a promo code, it comes back to 3 x R$ 7.37. If this change is not noticed, the user ends up paying more than they wanted to pay.
When you click to pay, a popup will appear offering a prime service for R$ 9.99 a month, with the option already selected. Many users have complained on Google Play and Apple Store about the R$ 9.99 fee they didn’t want due to their mistake of not realizing the option was already selected.
Solution
Don’t try to fool your users, have the interface follow the natural and intuitive way, do not pre-select options that will increase the cost for users, and never try to earn more by hiding fees or changing something users already selected how they want.
Avoid bad sales practices, they will hurt your reputation badly and will cost way more than what you’re earning with those bad practices.
Bonus: Confusing arrows

Well, UX is not only digital, it’s everything that communicates with your customer.
This one I saw the other day when in a department store in town.
In the store fitting room, you’re presented with three options: Women, Men, and Kids. But the arrows are all to the floor! A woman can be confused if she should go left or right there because even though the arrow is positioned at the right of the text (“provador feminino”, “women fitting room” in Portuguese), it’s not clear that’s the right side, especially since the arrows are slightly turned to the left.
Worse, no one was using the fitting room, so the customer didn’t even have a reference to follow a side since both were identical.
Solution
Don’t try to create something “cool” to impress users ending up forgetting the UX. Get your arrows straight in the right direction.
Worried about bad UI patterns?
Pengreen Design has an experienced team that offers design solutions for businesses to avoid bad UI patterns. We are also featured as one of the Top Mobile App Development Companies e Top Cross Platform Mobile App Development Companies.
Let’s talk about a Auditoria de UX and discover if your product has UX flaws
Não, designers não precisam necessariamente codificar. A menos que queiram se aprofundar nesta área, principalmente designers de interação, não é necessário que saibam codificar do zero uma interface. Mas é extremamente necessário entender o básico. Afinal, a interface é o elo entre a máquina e todo o funcionamento interno com o usuário leigo, portanto ela tem que falar ambas as línguas.
Os pontos principais que um designer precisa para pensar para melhorar seus trabalhos são:
Entender a estrutura: como meu design vai ser implementado? Em grid? Quantas colunas? Posso colocar um elemento num local específico?
Entender o responsivo (web) ou adaptativo (aplicativo móvel): Quais são os tamanhos de tela mais usados? Quais são as limitações de um smartphone? Como funciona os modos horizontais e verticais dos smartphones e tablets?
Work with technical possibilities and impossibilities: O que posso fazer? Não posso fazer? Isso é viável de ser implementado? Quais as consequências de implementar isso, vou atrapalhar a experiência do usuário para conseguir implementar o que eu projetei? Vou aumentar drasticamente o tempo de desenvolvimento?
Eficiência ao desenvolver:: What can I do differently that will deliver the same experience – or even better – but make development more efficient?

Os benefícios são percebidos por todos os envolvidos:
- Desenvolvedores: Eles vão agradecer ter uma interface feita com o código em mente, pois isto agiliza seu trabalho, não precisam implementar soluções diferentes que possam a causar bugs e alongar o projeto. Além disso, há menos possibilidade de de recair a culpa neles por não desenvolver como foi projetado.
- Usuários finais: a experiência destas pessoas será muito próxima àquela pretendida pelos designers, pois as diferenças entre o projeto gráfico e a entrega após o desenvolvimento diminuem e muito.
- Contratante: mais agilidade para receber o projeto, melhor retorno por entregar a experiência pretendida, e menos stress, tudo isso gera custos menores para quem solicitou o serviço.
Bônus: é possível assim desenvolver uma interface menos remendada e mais ágil, o que facilita futuros trabalhos e ajustes.
Resumindo
Mais rápido, mais limpo e melhores resultados no desenvolvimento, e uma experiência mais agradável para o usuário final.
Aqui na Pengreen Design, todos os nossos designers desenvolvem ou sabem o básico de desenvolvimento para que as interfaces sejam as melhores possíveis.
Gostaria de contar com uma equipe com designers experientes que desenvolvem as interfaces com o código em mente para que você terceirize o trabalho de design tenha um projeto eficiente? Conte com a gente! Somos reconhecidos como uma das principais empresas de design de experiência do usuário pelo DesignRush, seu projeto estará em boas mãos.